Sociological and archeological approaches
Here you can find sociohistorical material and archeological sites.
The schools of the founders
Academy of Plato and Aristotle's Lyceum




Proclus's house and school


The alleged prison of Socrates


On the way from Plato's Academy to Acropolis: Kerameikos

Poikile Stoa: The Stoic "meeting point"


Athen's Agora: Socrates' Teaching Ground
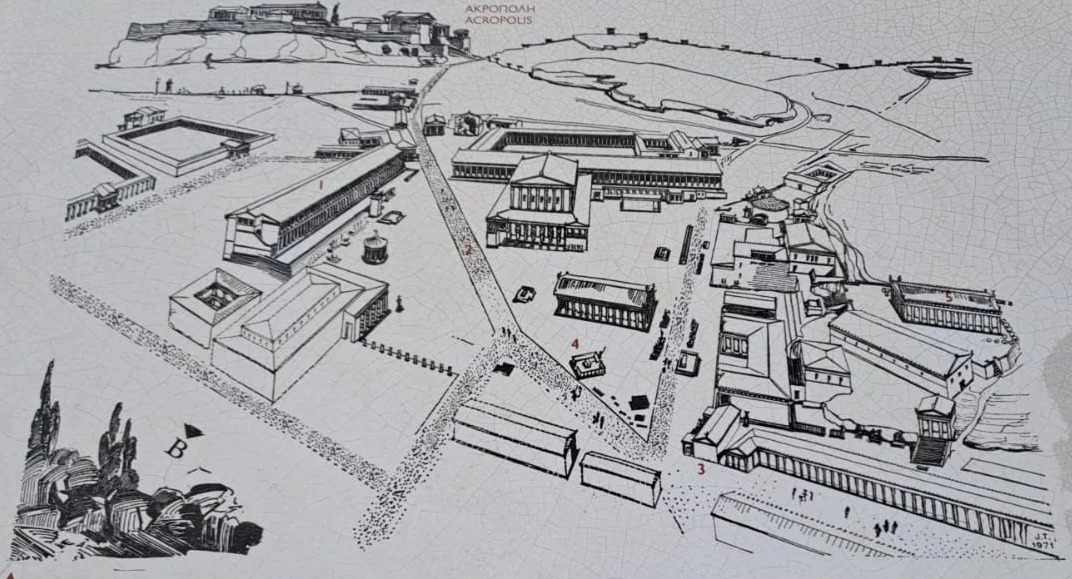

The Library of Hadrian


Philosophers of the Early Empire
Pythagoreans
Nigidus Figulus
Apollonius of Tyana
Moderatus of Gades
Nicomachus of Gerase
Epicureans
Dieogenes of Oenonanda
Philodemus
Academics/Platonists
Eudorus of Alexandria
Pseudo-Timaeus
Ammonius
Plutarch
Theon of Smyrna
Calvenus Taurus
Apuleius
Maximus of Tyre
Numenius of Apamea
Albinus
Alcinous
Atticus
Celsus
Peripatetics
Boethus of Sidon
Nicolaus of Damascus
Aspasius
Aristocles of Messana
Skeptics/Pyrrhonists
Agrippa
Sextus Empiricus
Cynics
Pseudo-Diogenes
Demetrius
Pseudo-Cebes
Dyo Chrysostom (Or Stoic)
Pseudo-Socrates
Pseudo-Heraclitus
Pseudo-Crates
Oenomaus of Gadara
Peregrinus Proteus
Demonax of Cyprus
Demetrius of Sunium
Theodorus
Stoics
Arius the Stoic
Late Stoa (Seneca)
Cornutus
Musonius Rufus
Epictetus
Hierocles
Marcus Aurelius
Bibliography
Afonasina, Anna & Afonasin, Eugene (2014). The Houses of Philosophical Schools in Athens. Schole 8 (1), 9-23.
Haake, Matthias (2007). Der Philosoph in der Stadt: Untersuchungen zur öffentlichen Rede über Philosophen und Philosophie in den hellenistischen Poleis, Vestigia 56, München: Beck.
Harrison, George W. M. and Francis, Jane (2008). "Plutarch in Crete". The Unity of Plutarch's Work: 'Moralia' Themes in the 'Lives', Features of the 'Lives' in the 'Moralia', edited by Anastasios G. Nikolaidis, Berlin, New York: De Gruyter, 791-804.
Sieben, Karen (2017). “Plato and Diogenes in Syracuse.” Politics and Performance in Western Greece: Essays on the Hellenic Heritage of Sicily and Southern Italy, edited by Heather L. Reid et al., vol. 2, Parnassos Press – Fonte Aretusa, 302–12.
Sterling, Gregory E.. (2017). "The School of Moses in Alexandria: An Attempt to Reconstruct the School of Philo". Second Temple Jewish “Paideia” in Context, edited by Jason M. Zurawski and Gabriele Boccaccini, Berlin, Boston: De Gruyter, 141-166.
Zovko, Marie-Élise (2017). “Of Caves, Lines, and Sea Travels: Plato’s Syracusan Voyages and the Central Analogies of the Republic.” Politics and Performance in Western Greece: Essays on the Hellenic Heritage of Sicily and Southern Italy, edited by Heather L. Reid et al., vol. 2, Parnassos Press – Fonte Aretusa, 313–28.
Further links:
Lyceum Aristotle ('home' for the peripatetics): https://goexploregreece.com/attica/athens/things-to-do/lyceum-of-aristotle/
The Location of the Houses of Cicero and Clodius and The Porticus Catuli on the Palatine Hill in Rome: https://muse.jhu.edu/article/1104/summary
